94 KiB
Spacemacs Documentation
Table of Contents
- Spacemacs Documentation
- Core Pillars
- Goals
- Screenshots
- Who can benefit from this ?
- Update and Rollback
- Configuration layers
- Dotfile Configuration
- Main principles
- Differences between Vim, Evil and Spacemacs
- Evil plugins
- Spacemacs UI
- Commands
- Vim key bindings
- Reserved prefix command for user
- Helm
- Discovering
- Navigating
- Searching
- Editing
- Registers
- Errors handling
- Compiling
- Modes
- Emacs Server
- Tips
- Achievements
- Thank you
Core Pillars
Four core pillars: Mnemonic, Discoverability, Consistency, "Crowd-Configured".
If any of these core pillars is violated open an issue and we'll fix it.
Mnemonic
Spacemacs organizes key bindings by mnemonic namespaces as much as possible.
If you are looking for commands to operate on your buffer, they are right under
SPC b, if you want to operate on your project, then it is
SPC p, etc...
Discoverability
Spacemacs comes with a dedicated major mode spacemacs-mode. Its goal is to
give useful feedbacks and easily perform maintenance tasks.
It also comes with dedicated [helm][] sources to quickly find layers, packages and more.
guide-key is enabled by default, it will display all the available key bindings in a dedicated popup buffer.
Consistency
Similar functionalities should have the same key binding no matter which major
is currently active. For instance if you are looking for the definition of a
function, the binding is SPC m g g, m for major mode and g g
for go to thing at point. No matter what is the major mode it is the same
binding to perform this action.
This is also true for the documentation, each configuration layer comes with
an associated README.md file with the same base layout.
The consistency core pillar is supported by a convention file: CONVENTIONS.md
Crowd-Configured
By defining an very light structure called configuration layer which is easy
to understand, Spacemacs makes it easy to contribute additional support.
The conventions in CONVENTIONS.md make it easy to get the spacemacs way and keep consistency even if there are a lot of contributions.
Crowd-configuration is the most powerful pillar of Spacemacs. Anybody can
submit upstream improvements to configuration layers or a whole new one. Any
user can easily and directly use this layer by adding it to a list in a
dotfile. It is even possible to exclude any unwanted packages.
Goals
-
Bring the power of modal editing to the powerful Emacs editing platform.
-
Integrate nicely with
Evilstates (Vimmodes):Spacemacstries to keep your fingers on the home row as much as possible, no matter the mode you are in. -
Crowed-configured: Contribute easily your improvements and new configuration layers.
-
Minimalistic and nice graphical UI, keep your available screen space for what matters: your text files.
-
Mnemonic and consistent key bindings which should be easier to learn and remember and be the same in all major modes.
-
Fast boot time, everything is lazy-loaded.
-
Lower the risk of RSI by heavily using the space bar instead of modifiers.
-
Hopefully, if it's not already the case:
Ɛ>Ɛ>Ɛ> make you love modal editing! <3<3<3
Screenshots
Note: Even though screenshots are updated frequently, Spacemacs is evolving
quickly and the screenshots may not reflect exactly the current state of the
project.
Who can benefit from this ?
Spacemacs is first intended to be used by Vim users who want to go to the
next level by using Emacs.
It is also a good fit for people wanting to lower the risk of RSI induced by the default Emacs key bindings (this is an assumption, there is no official studies to prove this).
Emacs users wanting to learn a different way to edit files or wanting to learn Vim key bindings.
As a side note, if you are a programmer and you don't know Vim key bindings yet, I deeply recommend you to learn the basics as recommended in Sacha Chua's one-page guide about how to learn Emacs.
Update and Rollback
For now it is still needed to update the Spacemacs repository manually.
Update Spacemacs repository
Close Emacs and update the git repository:
git pull --rebase
git submodule sync; git submodule update
Note It is recommended to update the packages first, see next session.
Update packages
To update Spacemacs press RET (enter) or click on the link
[Update] in the startup page under the banner then restart Emacs.
If anything goes wrong you should be able to rollback the update by pressing
RET or clicking on the [Rollback] link next to the [Update]
link and choose a rollback slot (sorted by date).
Configuration layers
Structure
Configuration is organized in layers. Each layer has the following structure:
[layer_name]
|__ [extensions]
| |__ [mode 1]
| | ...
| |__ [mode n]
|__ config.el
|__ extensions.el
|__ funcs.el
|__ keybindings.el
|__ packages.el
[] = directory
Where:
File | Usage
------------------|----------------------------------------------------------- config.el | Emacs built-in configuration or mandatory configuration extensions.el | The list of extensions to load and the functions to initialize them funcs.el | Various functions and macros (often used in keybindings.el) keybindings.el | Emacs built-in key bindings or mandatory key bindings packages.el | The list of packages to install and the functions to initialize them
Packages are ELPA packages which can be installed from an ELPA compliant
repository, and Extensions are generally elisp code from git submodules.
Extensions and Packages
Declaration
Extensions and Packages are declared in variables <layer>-pre-extensions,
<layer>-post-extensions and <layer>-packages where <layer> is the layer
name. Pre-Extensions are loaded before Packages and Post-Extensions are
loaded after Packages.
They are processed in alphabetical order so sometimes you'll have to use
some eval-after-load black magic.
Example:
(defvar <layer>-packages
'(
package1
package2
)
Initialization
To initialize an extension or a package xxx, define a function with this
format in extensions.el or packages.el:
(defun <layer>/init-xxx ()
...body
)
It is common to define the body with the use-package macro.
Exclusion
It is possible to exclude some packages from Spacemacs in a per layer basis.
This is useful when a configuration layer aims to replace a stock package
declared in the Spacemacs layer.
To do so add the package names to exclude to the variable
<layer>-excluded-packages.
Example:
(defvar <layer>-excluded-packages
'(
package1
)
Packages synchronization (Vundle like feature)
Spacemacs features a synchronization engine for the ELPA packages. It means
that Spacemacs will auto-install the new packages in <layer>-packages lists
and auto-delete orphan packages in your elpa directory.
It effectively makes Spacemacs behave like Vundle.
Types of configuration layers
There are three types of configuration layers:
- core (this is the
Spacemacslayer) - private (in the
privatedirectory, they are ignored by Git) - contrib (in the
contribdirectory, those layers are contributions shared by the community and merged upstream).
Submitting a configuration layer upstream
If you decide to provide a contrib configuration layer, please check
the contribution guidelines in CONTRIBUTE.md.
Example: Themes Megapack example
This is a simple contrib configuration layer listing a bunch of themes,
you can find it here.
To install it, just add themes-megapack to your ~/.spacemacs like so:
dotspacemacs-configuration-layers '(themes-megapack)
You have now installed around 100 themes you are free to try with SPC T h (helm-themes).
Managing private configuration layers
Spacemacs configuration system is flexible enough to let you manage your
private layers in different ways.
Using the private directory
Everything in the private directory is ignored by Git so it is a good place to store private layers. There is a huge drawback to this approach though: your layers are not source controlled.
Using an external Git repository
This is the recommended way to manage your private layers.
The best approach is to store all your private layers into an external Git
repository. It is especially a good practice to store them in your dotfiles
repository if you have one. Put also your ~/.spacemacs file in it.
Then you are free to symlink your layers into ~/emacs.d/private or let
them anywhere you want and reference the parent directory in the variable
dotspacemacs-configuration-layer-path of your ~/.spacemacs.
Note that you could also have a dedicated repository for all your private
layers and then directly clone this repository in ~/.emacs.d/private.
Using a personal branch
The final main way to manage your private layers is to push them in a personal
branch that you keep up to date with upstream master or develop.
Dotfile Configuration
User configuration can be stored in your ~/.spacemacs file.
Installation
~/.spacemacs is an optional file. If you want to use it you have to copy it
manually from the template file ~/.emacs.d/core/templates/.spacemacs.template
$ cp ~/.emacs.d/core/templates/.spacemacs.template ~/.spacemacs
Content
Using configuration layers
To use a configuration layer, add it to the dotspacemacs-configuration-layers
variable of your ~/.spacemacs.
For instance to add the configuration layer of RMS:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-configuration-layers '(rms))
If this layer does not exist you can still try another one in
the contrib directory.
Configuration layers are expected to be stored in ~/.emacs.d/private or
~/.emacs.d/contrib. But you are free to keep them somewhere else by declaring
additional paths where Spacemacs can look for configuration layers.
This is done by setting the list
dotspacemacs-configuration-layer-path in your ~/.spacemacs:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-configuration-layer-path '("~/.myconfig/"))
Setting configuration layers variables
Some configuration layers have configuration variables to enable specific
support. For instance the git layer has several configuration variables,
they can be set directly in the dotspacemacs-configuration-layers like this:
;; List of configuration layers to load.
dotspacemacs-configuration-layers '(company-mode
(git :variables
git-magit-status-fullscreen t
git-enable-github-support t
git-gutter-use-fringe t)
smex)
Excluding packages
You can exclude packages you don't want to install with the variable
dotspacemacs-excluded-packages, this variable can exclude both packages and
extensions (see Configuration layers for more info
on packages and extensions).
For instance to disable the rainbow-delimiters package:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-excluded-packages '(rainbow-delimiters))
When you exclude a package, Spacemacs will automatically delete it for you
the next time you launch Emacs. All the orphan dependencies are as well
delete automatically.
Hooks
Two special functions of the ~/.spacemacs file can be used to perform
configuration at the beginning and end of Spacemacs loading process.
dotspacemacs/initis triggered at the very beginning ofSpacemacsloading.dotspacemacs/configis triggered at the very end ofSpacemacsloading.
Custom variables
Custom variables configuration from M-x customize-group which are
automatically saved by Emacs are stored at the end of your ~/.spacemacs
file.
Main principles
Evil
Spacemacs uses the evil mode to emulate Vim key bindings. It is a
very complete emulation, maybe the most advanced. In fact, Evil is much more
than just a Vim emulation. It has more states than Vim for instance.
States
Spacemacs has 8 states:
- Normal (orange) - like the
normal mode of Vim, used to execute and combine commands - Insert (green) - like the
insert mode of Vim, used to actually insert text - Visual (gray) - like the
visual mode of Vim, used to make text selection - Motion (purple) - exclusive to
Evil, used to navigate read only buffers - Emacs (blue) - exclusive to
Evil, using this state is like using a regular Emacs without Vim - Lisp (pink) - exclusive to
Spacemacs, used to navigate Lisp code and modify it (see Editing Lisp code) - Iedit (red) - exclusive to
Spacemacs, used to navigate between multiple regions of text usingiedit(see Replacing text with iedit) - Iedit Insert (red) - exclusive to
Spacemacs, used to replace multiple regions of text usingiedit(see Replacing text with iedit)
Note: Technically speaking there are also the operator and replace evil
states.
Evil leader
Spacemacs heavily uses the evil-leader mode which brings the
Vim leader key to the Emacs world.
This leader key is commonly set to , by Vim users, in Spacemacs the leader
key is set on SPC (space bar, this is why the name spacemacs).
This key is the most accessible key on a keyboard and it is pressed with the
thumb which is a good choice to lower the risk of RSI.
So with Spacemacs there is no need to remap your keyboard modifiers to
attempt to reduce the risk of RSI, every command can be executed very easily
while you are in normal mode by pressing the SPC leader key,
here are a few examples:
- Save a buffer: SPC f s
- Save all opened buffers: SPC f S
- Open (switch) to a buffer with
helm: SPC b s
Universal argument
The universal argument C-u is an important command in Emacs but it is also
a very handy Vim key binding to scroll up.
Spacemacs binds C-u to scroll-up and change the universal
argument binding to SPC u.
Micro-states
Spacemacs defines a wide variety of micro-states (temporary overlay maps)
where it makes sense. This prevents one from doing repetitive and tedious presses on the
SPC key.
When a micro-state is active, a documentation is displayed in the minibuffer.
Additional information may as well be displayed in the minibuffer.
Auto-highlight-symbol micro-state:
Differences between Vim, Evil and Spacemacs
No doubt that Evil is one of the most advanced Vim emulation and you should
not see big difference between Vim and Emacs. I did not find any command I
used in Vim that I missed in Emacs with Evil.
Send a PR to add the differences you found in this section.
The vim-surround case
There is one obvious visible difference though. It is not between Evil and
Vim but between Spacemacs and vim-surround: the surround command is
on S in vim-surround whereas it is on s in Spacemacs.
This is something that can surprise some Vim users so let me explain why this is the case:
sandcdo the same thing invisual state,sis only useful to delete one character and add more than one character which is a very narrow use case,caccept motions and can do everythingscan do innormal state,- this is also true for
rbutris more useful because it stays innormal state. surroundcommand is just a more powerful command thans
If you are not convinced, then here is the snippet to revert back to the default
Vim + vim-surround setup (add it to your dotspacemacs/config function or
your ~/.spacemacs):
(evil-define-key 'visual evil-surround-mode-map "s" 'evil-substitute)
(evil-define-key 'visual evil-surround-mode-map "S" 'evil-surround-region)
Evil plugins
Spacemacs ships with the following evil plugins:
Mode | Description
----------------------------------------|--------------------------------------
evil-leader | vim leader that bring a new layer of keys in normal mode
evil-indent-textobject | add text object based on indentation level
evil-visualstar | search for current selection with *
evil-exchange | port of vim-exchange
evil-surround | port of vim-surround
evil-matchit | port of matchit.vim
evil-nerd-commenter | port of nerdcommenter
[evil-search-highlight-persist][] | emulation of hlsearch behavior
evil-numbers | like C-a/C-x in vim
evil-args | motions and text objects for arguments
evil-jumper | jump list emulation
NeoTree | mimic NERD Tree
Spacemacs UI
Spacemacs has unique UI elements to make the Emacs experience even
more enjoyable:
- dedicated startup page with a mode aimed at easily managing
Spacemacs - dedicated helm source via
helm-spacemacs - a guide-key buffer
Graphical UI
Spacemacs has a minimalistic and distraction free graphical UI:
- custom powerline mode-line with color feedback according to current Flycheck status
- unicode symbols for minor mode lighters which appear in the mode-line
- custom fringe bitmaps and error feedbacks for Flycheck
- custom fringe bitmaps for git gutter (available in git layer)
Color themes
By default, Spacemacs uses the theme solarized-light.
It is possible to define your default themes in your ~/.spacemacs with
the variable dotspacemacs-themes. For instance, to specify leuven and
zenburn (high contrast theme and low contrast theme):
(setq-default dotspacemacs-themes '(leuven zenburn))
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
SPC T n | switch to next theme listed in dotspacemacs-themes.
SPC T h | select a theme using a helm buffer.
Note: Due to the inner working of themes in Emacs, switching theme during the same session may have some weird side effects. Although these side effects should be pretty rare.
Hint If you are an Org user, leuven-theme is amazing ;-)
Font
The default font used by Spacemacs is source code pro by Adobe. It is
recommended to install it on your system.
To change the default font set the variable dotspacemacs-default-font in
your .spacemacs file.
By default its value is:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-default-font '("Source Code Pro"
:size 13
:weight normal
:width normal
:powerline-scale 1.1))
The properties should be pretty straightforward, it is possible to set any valid property of a font-spec:
:familyFont family or fontset (a string).:widthRelative character width. This should be one of the symbols:- ultra-condensed
- extra-condensed
- condensed
- semi-condensed
- normal
- semi-expanded
- expanded
- extra-expanded
- ultra-expanded
:heightThe height of the font. In the simplest case, this is an integer in units of 1/10 point.:weightFont weight—one of the symbols (from densest to faintest):- ultra-bold
- extra-bold
- bold
- semi-bold
- normal
- semi-light
- light
- extra-light
- ultra-light
:slantFont slant—one of the symbols:- italic
- oblique
- normal
- reverse-italic
- reverse-oblique
:sizeThe font size—either a non-negative integer that specifies the pixel size, or a floating-point number that specifies the point size.:adstyleAdditional typographic style information for the font, such as ‘sans’. The value should be a string or a symbol.:registryThe charset registry and encoding of the font, such as ‘iso8859-1’. The value should be a string or a symbol.:scriptThe script that the font must support (a symbol).
The special property :powerline-scale is Spacemacs specific and it is for
quick tweaking of the mode-line height in order to avoid crappy rendering of
the separators like on the following screenshot (default value is 1.1).
Ugly separators
Graphical UI Toggles
Some graphical UI indicators can be toggled on and off (toggles start with t):
Key Binding | Description
----------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC t 8 | display a mark on the 80th column SPC t F | toggle frame fullscreen SPC t f | toggle display of the fringe SPC t h | toggle highlight of the current line SPC t i | toggle aggressive indent SPC t l | toggle truncate lines SPC t L | toggle visual lines SPC t M | toggle frame maximize SPC t n | show the absolute line numbers SPC t t | toggle frame transparency SPC t T | toggle tool bar SPC t U | toggle menu bar
Note These toggles are all available via the helm-spacemacs interface
(press SPC fe h to display the helm-spacemacs buffer).
Mode-line
The mode line is a heavily customized powerline with the following capabilities:
- show the window number
- color code for current state
- show the number of search occurrences via anzu
- toggle flycheck info
- toggle battery info
- toggle minor mode lighters
Reminder of the color codes for the states:
| Evil State | Color |
|---|---|
| Normal | Orange |
| Insert | Green |
| Visual | Grey |
| Emacs | Blue |
| Motion | Purple |
| Lisp | Pink |
| Iedit/Iedit-Insert | Red |
Some elements can be dynamically toggled:
Key Binding | Description
-----------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC t m m | toggle the minor mode lighters SPC t m b | toggle the battery status SPC t m f | toggle the flycheck info SPC t m v | toggle the new version lighter
Flycheck integration
When Flycheck minor mode is enabled, a new element appears showing the number of errors, warnings and info.
Anzu integration
Anzu shows the number of occurrence when performing a search. Spacemacs
integrates nicely the Anzu status by displaying it temporarily when n or N are
being pressed. See the 5/6 segment on the screenshot below.
Battery status integration
fancy-battery displays the percentage of total charge of the battery as well as the time remaining to charge or discharge completely the battery.
A color code is used for the battery status:
| Battery State | Color |
|---|---|
| Charging | Green |
| Discharging | Orange |
| Critical | Red |
Note the these colors may vary depending on your theme.
Powerline separators
It is possible to easily customize the powerline separator by setting the
powerline-default-separator variable in your ~./spacemacs. For instance
if you want to set back the separator to the well-known arrow separator
add the following snippet to your configuration file:
(defun dotspacemacs/config ()
"This is were you can ultimately override default Spacemacs configuration.
This function is called at the very end of Spacemacs initialization."
(setq powerline-default-separator 'arrow)
)
To save you the time to try all the possible separators provided by the powerline, here is an exhaustive set of screenshots:
Separator | Screenshot
------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
alternate | 
arrow | 
arrow-fade | 
bar | 
box | 
brace | 
butt | 
chamfer | 
contour | 
curve | 
rounded | 
roundstub | 
slant | 
wave | 
zigzag | 
nil | 
Minor Modes
Spacemacs uses diminish mode to reduce the size of minor mode
indicators:
The minor mode area can be toggled on and off with:
<SPC> t m m
Unicode symbols are displayed by default. Setting the variable
dotspacemacs-mode-line-unicode-symbols to nil in your ~/.spacemacs will
display ASCII characters instead (may be useful in terminal).
| Unicode | ASCII | Mode |
|---|---|---|
⊞ |
G | golden-ratio mode |
Ⓐ |
A | auto-complete mode |
Ⓒ |
C | centered-cursor mode |
Ⓔ |
E | evil-org mode |
Ⓕ |
F | flycheck mode |
Ⓚ |
K | guide-key mode |
Ⓘ |
I | aggressive indent mode |
(Ⓟ) |
(P) | paredit mode |
Ⓢ |
S | flyspell mode |
(Ⓢ) |
(S) | smartparens mode |
Ⓦ |
W | whitespace mode |
Ⓨ |
Y | yasnippet mode |
Commands
Vim key bindings
Spacemacs is based on Vim modal user interface to navigate and edit text.
If you are not familiar with the Vim way of editing text you can try the
[evil tutor][] lessons by pressing SPC h T at any time.
Escaping
Spacemacs uses evil-escape to easily switch between insert state and
normal state by quickly pressing the fd keys.
The choice of fd was made to be able to use the same sequence to escape from
"everything" in Emacs:
- escape from all evil states to normal state
- escape from evil-lisp-state to normal state
- abort evil ex command
- quit minibuffer
- abort isearch
- quit magit buffers
- quit help buffers
- quit apropos buffers
- quit ert buffers
- quit undo-tree buffer
- quit paradox
- quit gist-list menu
- hide neotree buffer
This sequence can be customized in your ~/.spacemacs. Example to set it
to jj (it is important set the variable in dotspacemacs/init):
(defun dotspacemacs/init ()
(setq-default evil-escape-key-sequence "jj"))
Note: Although jj or jk are popular choices of vim users, these key
sequences are not optimal for Spacemacs. Indeed it is very easy in
visual state to press quickly jj and inadvertently escape to normal state.
Executing Vim and Emacs ex/M-x commands
Command | Key Binding
:---------------:|------------------------------------------------------------------
Vim (ex-command) | :
Emacs (M-x) | SPC :
The command key : can be easily changed with the variable
dotspacemacs-command-key of your ~/.spacemacs. Note that is will change both
: and SPC : bindings to keep the symmetry between Vim and Emacs. A good
key can be , for example.
Leader key
On top of Vim modes (modes are called states in Spacemacs) there is a
special key called the leader key which once pressed gives a whole new
keyboard layer. The leader key is by default SPC (space).
It is possible to change this key with the variable dotspacemacs-leader-key.
Reserved prefix command for user
SPC o is reserved for the user. Setting key bindings behind
<SPC> o is guaranteed to never conflict with Spacemacs defaults key
bindings.
Helm
Spacemacs is powered by Helm which is an incremental completion
and selection narrowing framework.
Helm is the central control tower of Spacemacs, it is used to manage
buffers, projects, search results, configuration layers, toggles and more...
Mastering Helm will make you a Spacemacs power user. Do not hesitate
to read the Helm documentation wiki.
Helm micro-state
Spacemacs defines a micro-state for Helm to make it
work like Vim's Unit plugin.
Initiate the micro-state with C-SPC while in a Helm buffer.
Use C-SPC again to exit from the micro-state.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| C-SPC | initiate or leave the micro-state |
| TAB | switch to actions page and leave the micro-state |
| 1 | execute action 0 |
| 2 | execute action 1 |
| 3 | execute action 2 |
| 4 | execute action 3 |
| 5 | execute action 4 |
| 6 | execute action 5 |
| 7 | execute action 6 |
| 8 | execute action 7 |
| 9 | execute action 8 |
| 0 | execute action 9 |
| a | switch to actions page |
| g | go to first candidate |
| G | go to last candidate |
| h | go to previous source |
| j | select next candidate |
| k | select previous candidate |
| l | go to next source |
| t | mark current candidate |
| T | mark all candidates |
| v | execute persistent action |
Discovering
Key bindings
An help buffer is displayed each time the SPC key is pressed in normal mode. It lists the available key bindings and their associated commands.
By default the guide-key buffer will be displayed quickly after the key
has been pressed. You can change the delay by setting the variable
dotspacemacs-guide-key-delay to your liking (the value is in second).
Available layers
All layers can be easily discovered via helm-spacemacs accessible with
SPC f e h.
The following helm actions are available:
- default: open the layer
README.md - 2nd: open the layer
packages.el - 3nd: open the layer
extensions.el
Available packages in Spacemacs
helm-spacemacs also lists all the packages available in Spacemacs.
The entry format is (layer) packages. If you type flycheck you'll
be able to see all the layers where flycheck is used.
The following helm actions are available on packages:
- default: go the package init function
New packages from ELPA repositories
package-list-packages is where you can browse for all available packages
in the different Elpa repositories. It is possible to upgrade packages
from there but it is not recommended, use the [Update] link on the
Spacemacs startup page instead.
Spacemacs proposes to use Paradox instead of package-list-packages
to list available ELPA packages.
Paradox enhances the package list buffer with better feedbacks, new
filters and Github information like the number of stars. Optionally you
can also star packages directly in the buffer.
Important Note 1 Installing a new package from Paradox won't make it
persistent. To install a package persistently you have to add it explicitly
to a configuration layer.
Important Note 2 Don't update your packages from Paradox or
package-list-packages because they don't support the rollback feature of
Spacemacs.
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
/ | evil-search
f k | filter by keywords
f r | filter by regexp
f u | display only installed package with updates available
h | go left
H | show help (not accurate)
j | go down
k | go up
l | go right
L | show last commits
n | next search occurrence
N | previous search occurrence
o | open package homepage
r | refresh
S P | sort by package name
S S | sort by status (installed, available, etc...)
S * | sort by Github stars
v | visual state
V | visual-line state
x | execute (action flags)
Toggles
helm-spacemacs is also a central place to discover the available toggles.
To display only the toggles source press C-l (or in
Helm micro-state you can press just l).
The following helm actions are available on packages:
- default: toggle on/off
Tips Use SPC h l to resume the last helm session. It is handy to quickly toggle on and off a toggle.
Navigating
Point/Cursor
Navigation is performed using the Vi key bindings hjkl.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
h |
move cursor left |
j |
move cursor down |
k |
move cursor up |
l |
move cursor right |
H |
move quickly up (10 lines at a time) |
L |
move quickly down (10 lines at a time) |
| SPC j h | go to the beginning of line (and set a mark at the previous location in the line) |
| SPC j l | go to the end of line (and set a mark at the previous location in the line) |
| SPC z z | lock the cursor at the center of the screen |
Smooth scrolling
smooth-scrolling prevent the point to jump when it reaches the top or bottom of the screen. It is enabled by default.
On Windows, you may want to disable it. To disable the smooth scrolling set
the dotspacemacs-smooth-scrolling variable in your ~/.spacemacs to nil:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-smooth-scrolling t)
Vim motions with ace-jump mode
Spacemacs uses the evil integration of ace-jump mode which
enables the invocation of ace-jump-mode during motions.
It is useful for deleting visually a set of lines, try the following sequence in a buffer containing some text:
d <SPC> l
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC SPC | initiate ace jump word mode |
| SPC l | initiate ace jump line mode |
| SPC ` | go back to the previous location (before the jump) |
Hint: you may change to char mode by C-c C-c in word mode.
Window manipulation
Window manipulation key bindings
Every window has a number displayed at the start of the mode-line and can
be quickly accessed using <SPC> number.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC 1 | go to window number 1 |
| SPC 2 | go to window number 2 |
| SPC 3 | go to window number 3 |
| SPC 4 | go to window number 4 |
| SPC 5 | go to window number 5 |
| SPC 6 | go to window number 6 |
| SPC 7 | go to window number 7 |
| SPC 8 | go to window number 8 |
| SPC 9 | go to window number 9 |
| SPC 0 | go to window number 0 |
Windows manipulation commands (start with w):
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC w b | force the focus back to the minibuffer (usefull with helm popups) |
| SPC w c | close a window |
| SPC w C | close other windows |
| SPC w d | toggle window dedication (dedicated window cannot be reused by a mode) |
| SPC w h | move to window on the left |
| SPC w H | move window to the left |
| SPC w j | move to window below |
| SPC w J | move window to the bottom |
| SPC w k | move to window above |
| SPC w K | move window to the top |
| SPC w l | move to window on the right |
| SPC w L | move window to the right |
| SPC w m | maximize/minimize a window |
| SPC w M | maximize/minimize a window, when maximized the buffer is centered |
| SPC w o | cycle and focus between frames |
| SPC w p m | open messages buffer in a popup window |
| SPC w p p | close the current sticky popup window |
| SPC w R | rotate windows clockwise |
| SPC w s or SPC w / | horizontal split |
| SPC w S | horizontal split and focus new window |
| SPC w u | undo window layout (used to effectively undo a closed window) |
| SPC w U | redo window layout |
| SPC w v or SPC w - | vertical split |
| SPC w V | vertical split and focus new window |
| SPC w w | cycle and focus between windows |
Window manipulation micro-state
A convenient window manipulation micro-state allows to perform most of the actions listed above. The micro-state allows additional actions as well like window resizing.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC w . | initiate micro-state |
| ? | display the full documentation in minibuffer |
| 0 | go to window number 0 |
| 1 | go to window number 1 |
| 2 | go to window number 2 |
| 3 | go to window number 3 |
| 4 | go to window number 4 |
| 5 | go to window number 5 |
| 6 | go to window number 6 |
| 7 | go to window number 7 |
| 8 | go to window number 8 |
| 9 | go to window number 9 |
| - | vertical split |
| / | horizontal split |
| [ | shrink window horizontally |
| ] | enlarge window horizontally |
| { | shrink window vertically |
| } | enlarge window vertically |
| c | close window |
| C | close other windows |
| g | toggle golden-ratio on and off |
| h | go to window on the left |
| j | go to window below |
| k | go to window above |
| l | go to window on the right |
| H | move window to the left |
| J | move window to the bottom |
| K | move bottom to the top |
| L | move window to the right |
| o | focus other frame |
| R | rotate windows |
| s | horizontal split |
| S | horizontal split and focus new window |
| u | undo window layout (used to effectively undo a closed window) |
| U | redo window layout |
| v | vertical split |
| V | horizontal split and focus new window |
| w | focus other window |
| Any other key | leave the micro-state |
Golden ratio
If you resize windows like crazy you may want to give a try to golden-ratio.
golden-ratio resizes windows dynamically depending on whether they are
selected or not. By default golden-ratio is off.
The mode can be toggled on and off with:
<SPC> t g
Buffers and Files
Spacemacs uses ido for opening files since ido way to navigate
the file system is better than helm in my opinion (especially because ido can
remember the last selected directories and buffers, maybe helm can do this ?).
ido is also used to kill buffers.
Buffer manipulation commands (start with b):
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC b 0 | move to the beginning of buffer (useful in emacs state buffers) |
| SPC b $ | move to the end of buffer (useful in emacs state buffers) |
| SPC b b or SPC TAB | switch to alternate buffer (switch back and forth) |
| SPC b e | erase the content of the buffer (ask for confirmation) |
| SPC b k | kill the current buffer |
| SPC b K | kill all buffers except the current one |
| SPC b C-K | kill all buffers matching the regexp |
| SPC b m h | move a buffer to the left |
| SPC b m j | move a buffer to the bottom |
| SPC b m k | move a buffer to the top |
| SPC b m l | move a buffer to the right |
| SPC b n | switch to next buffer |
| SPC b p | switch to previous buffer |
| SPC b r | rename the current buffer |
| SPC b R | revert the current buffer (reload from disk) |
| SPC b s | switch to a buffer using helm |
| SPC b w | toggle read-only (writable state) |
| z f | Make current function or comments visible in buffer as much as possible |
Files manipulation commands (start with f):
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC f D | delete a file and the associated buffer (ask for confirmation) |
| SPC f f | open a file using ido |
| SPC f j | jump to the current buffer file in dired |
| SPC f o | open a file using the default external program |
| SPC f s | save a file |
| SPC f S | save all files |
| SPC f r | open a recent file with helm |
| SPC f t | toggle file tree side bar using NeoTree |
| SPC f y | show current file absolute path in the minibuffer |
Emacs and Spacemacs files
Convenient key bindings are located under the prefix SPC f e to
quickly navigate between Emacs and Spacemacs specific files.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC f e c | open ido in the contrib folder |
| SPC f e d | open the spacemacs dotfile (~/.spacemacs) |
| SPC f e h | discover Spacemacs layers and packages using helm |
| SPC f e i | open the all mighty init.el |
| SPC f e s | open ido in the spacemacs layer folder |
Ido
Spacemacs displays the ido minibuffer vertically thanks to the
ido-vertical-mode.
Basic ido operations can be done with Ctrl key:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| C-<return> | open a dired buffer |
| M-<return> | open a dired buffer in terminal |
| C-d | delete selected file (ask for confirmation) |
| C-h | go to parent directory |
| C-j | select next file or directory |
| C-S-j | go to next directory |
| C-k | select previous file or directory |
| C-S-k | go to previous directory |
| C-l | open the selected file |
| C-n | next history element |
| C-o | open selected file in other window |
| C-p | previous history element |
| C-s | open selected file in a vertically split window |
| C-t | open selected file in a new frame |
| C-v | open selected file in a horizontally split window |
Ido micro-state
Spacemacs defines a micro-state for ido.
Initiate the micro-state with C-SPC while in a ido buffer.
Use C-SPC again to exit from the micro-state.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| C-SPC | initiate or leave the micro-state |
| ? | display help |
| e | open dired |
| h | delete backward or parent directory |
| j | next match |
| J | sub directory |
| k | previous match |
| K | parent directory |
| l | select match |
| n | next directory in history |
| o | open in other window |
| p | previous directory in history |
| s | open in a new horizontal split |
| t | open in other frame |
| v | open in a new vertical split |
NeoTree file tree
Spacemacs provides a quick and simple way to navigate in an unknown project
file tree with NeoTree.
To toggle the NeoTree buffer press:
<SPC> f t
The NeoTree window always has the number 0 so it does not shift the current
number of the other windows. To select the NeoTree window you then use
SPC 0.
NeoTree navigation
Navigation is centered on the hjkl with the hope to provide a fast navigation
experience like in [ranger][]:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| h | collapse expanded directory or go to parent node |
| H | previous sibling |
| j | next file or directory |
| J | next expanded directory on level down |
| k | previous file or directory |
| K | parent directory, when reaching the root change it to parent directory |
| l or RET | expand directory |
| L | next sibling |
Note: The point is automatically set to the first letter of a node for a smoother experience.
Opening files with NeoTree
By default a file is opened in the last active window. It is possible to choose window number where to open a file by using a numeric argument, for instance 2 l or 2 RET will open the current file in the windows 2. It is also possible to open the file in a split window with | and -:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| l or RET | open file in last active window |
| # l or 2 RET | open file in window number # |
| | | open file in an vertically split window |
| - | open file in an horizontally split window |
Other NeoTree key bindings
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| TAB | toggle stretching of the buffer |
| c | create a node |
| d | delete a node |
| g | refresh |
| s | toggle showing of hidden files |
| q or fd | hide NeoTree buffer |
| r | rename a node |
NeoTree mode-line
The mode-line has the following format [x/y] d (D:a, F:b) where:
xis the index of the current selected file or directoryythe total number of items (file and directory) in the current directorydthe name of the current directoryathe number of directories in the current directorybthe number of files in the current directory
Shells
Key bindings
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| C-j | next item in history |
| C-k | previous item in history |
| SPC m h | browse history with helm (works in eshell and shell) |
Staying in insert state
Navigating in shell buffers can be tricky because it is not possible to use the
leader in insert state. Switching back and forth between normal and insert
states can be tedious. The solution to this is to use C-o then use
the leader key. C-o set the next key to be evaluated in
normal state.
Bookmarks
Bookmarks can be set anywhere in a file. Bookmarks are persistent. They are very
useful to jump to/open a known project. Spacemacs used helm-bookmarks to
manage them.
Open an helm window with the current bookmarks by pressing:
<SPC> h b
Then in the helm-bookmarks buffer:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| CTRL+d | delete the selected bookmark |
| CTRL+e | edit the selected bookmark |
| CTRL+f | toggle filename location |
| CTRL+o | open the selected bookmark in another window |
To save a new bookmark, just type the name of the bookmark and press RET.
DocView mode
doc-view-mode is a built-in major mode to view DVI, PostScript (PS), PDF,
OpenDocument, and Microsoft Office documents.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| / | search forward |
| ? | search backward |
| + | enlarge |
| - | shrink |
| gg | go to first page |
| G | go to last page |
| h | previous page |
| H | adjust to height |
| j | next line |
| k | previous line |
| K | kill proc and buffer |
| l | next page |
| n | go to next search occurrence |
| N | go to previous search occurrence |
| P | fit page to window |
| r | revert |
| W | adjust to width |
| C-d | scroll down |
| C-k | kill proc |
| C-u | scroll up |
| C-c C-c | toggle display text and image display |
| C-c C-t | open new buffer with doc's text contents |
Searching
Project Searching
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC / or SPC a | with The Silver Searcher |
| SPC A | with ack |
| SPC g | with grep |
| SPC h l | show last helm popup |
Persistent highlighting
Spacemacs uses evil-search-highlight-persist to keep the searched expression
highlighted until the next search. It is also possible to clear the
highlighting by pressing SPC s c or executing the ex command :noh.
Stacking highlights
With [hl-anything][] it is possible to highlight all occurrences of the word under point. The highlights can be stacked.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC h c | clear the highlightings |
| SPC h g c | clear the highlightings globally (all opened buffers) |
| SPC h h | highlight all occurrence of the word at point |
| SPC h g h | highlight all occurrence of the word at point globally (all opened buffers) |
| SPC h n | next highlighted occurrence |
| SPC h N | previous highlighted occurrence |
| SPC h p | toggle auto-highlight of the enclosing parenthesis |
| SPC h r | restore saved highlights in the current buffer |
| SPC h s | save current highlights |
Highlight current symbol
Spacemacs supports highlighting of the current symbol on demand (provided by
the auto-highlight-symbol mode) and adds a micro-state to
easily navigate and rename this symbol.
It is also possible to change the range of the navigation on the fly to:
- buffer
- function
- visible area
To initiate the highlighting of the current symbol under point press SPC s h.
Navigation between the highlighted symbols can be done with the commands:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| * | initiate navigation micro-state on current symbol and jump forwards |
| # | initiate navigation micro-state on current symbol and jump backwards |
| SPC s b | go to the last searched occurrence of the last highlighted symbol |
| SPC s e | edit all occurrences of the current symbol(*) |
| SPC s h | highlight the current symbol and all its occurrence within the current range |
| SPC s R | change range to default (whole buffer) |
In 'Spacemacs' highlight symbol micro-state:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| e | edit occurrences (*) |
| n | go to next occurrence |
| N | go to previous occurrence |
| d | go to next definition occurrence |
| D | go to previous definition occurrence |
| r | change range (function, display area, whole buffer) |
| R | go to home occurrence (reset position to starting occurrence) |
| Any other key | leave the navigation micro-state |
(*) using iedit or the default implementation of auto-highlight-symbol
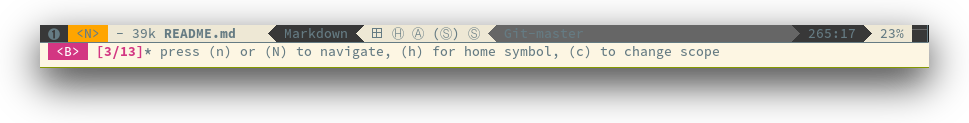
The micro-state text in minibuffer display the following information:
<M> [6/11]* press (n/N) to navigate, (e) to edit, (r) to change range or (R) for reset
Where <M> [x/y]* is:
- M: the current range mode
<B>: whole buffer range<D>: current display range<F>: current function range
x: the index of the current highlighted occurrencey: the total number of occurrences*: appears if there is at least one occurrence which is not currently visible.
Visual Star
With evil-visualstar you can search for the next occurrence of the current selection.
It is pretty useful combined with the expand-region bindings.
Note: If the current state is not the visual state then pressing * uses
auto-highlight-symbol and its micro-state.
Listing symbols by semantic
Use helm-semantic-or-imenu command from Helm to quickly navigate between
the symbols in a buffer.
To list all the symbols of a buffer press:
<SPC> s l
Helm-swoop
This is very similar to moccur, it displays a helm buffer with all the
occurrences of the word under point. You can then change the search query
in real-time and navigate between them easily.
You can even edit the occurrences directly in the helm buffer and apply
the modifications to the buffer.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC s s | execute helm-swoop |
| SPC s S | execute helm-multi-swoop |
| SPC s C-s | execute helm-multi-swoop-all |
Editing
Text manipulation commands
Text related commands (start with x):
Key Binding | Description
-----------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC x u | set the selected text to lower case SPC x U | set the selected text to upper case SPC x d w | delete trailing whitespaces SPC x g l | set languages used by translate commands SPC x g t | translate current word using Google Translate SPC x g T | reverse source and target languages SPC x m j | move down a line of text SPC x m k | move up a line of text SPC x t c | swap (transpose) the current character with the previous one SPC x t w | swap (transpose) the current word with the previous one SPC x t l | swap (transpose) the current line with the previous one SPC x w c | count the number of words in the selection region SPC x w C | count the number of occurrences per word in the select region
Smartparens Strict mode
Smartparens comes with a strict mode which prevents deletion of parenthesis if the result is unbalanced.
This mode can be frustrating for novices, this is why it is not enabled by default.
It is possible to enable it easily for all programming modes with the
variable dotspacemacs-smartparens-strict-mode of you ~/.spacemacs.
(setq-default dotspacemacs-smartparens-strict-mode t)
Zooming
Text
The font size of the current buffer can be adjusted with the commands:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
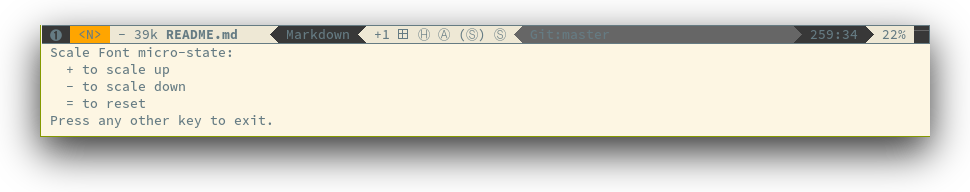
| SPC z x + | scale up the font and initiate the font scaling micro-state |
| SPC z x - | scale down the font and initiate the font scaling micro-state |
| SPC z x = | reset the font size (no scaling) and initiate the font scaling micro-state |
| + | increase the font size |
| - | decrease the font size |
| = | reset the font size |
| Any other key | leave the font scaling micro-state |
Note that only the text of the current buffer is scaled, the other buffers,
the mode-line and the minibuffer are not affected. To zoom the whole content of
a frame use the zoom frame bindings (see next section).
Frame
You can zoom in and out the whole content of the frame with the commands:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC z f + | zoom in the frame content |
| SPC z f - | zoom out the frame content |
| SPC z f = | reset the frame content size |
| + | zoom in |
| - | zoom out |
| = | reset zoom |
| Any other key | leave the zoom frame micro-state |
Increase/Decrease numbers
Spacemacs uses evil-numbers to easily increase or increase numbers.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC n + | increase the number under point by one and initiate micro-state |
| SPC n - | decrease the number under point by one and initiate micro-state |
In micro-state:
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| + | increase the number under point by one |
| - | decrease the number under point by one |
| Any other key | leave the micro-state |
Tips: you can increase or decrease a value by more that once by using a
prefix argument (ie. 10 SPC n + will add 10 to the number under point).
Spell checking
Spell checking commands start with S:
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
SPC S c | list of corrections in a helm buffer
SPC S d | change dictionary language
SPC S n | go to the next spell check error
Region selection
Vi Visual modes are all supported by evil.
Expand-region
Spacemacs adds another Visual mode via the expand-region mode.
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC v | initiate expand-region mode then... |
| v | expand the region by one semantic unit |
| V | contract the region by one semantic unit |
| r | reset the region to initial selection |
| ESC | leave expand-region mode |
Indent text object
With evil-indent-textobject the following action can be performed in
normal state:
- ii - Inner Indentation: the surrounding textblock with the same indentation
- ai - Above and Indentation: ii + the line above with a different indentation
- aI - Above and Indentation+: ai + the line below with a different indentation
Example (| is the point):
(while (not done)
(messa|ge "All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy."))
(1+ 41)
- vii will select the line with message
- vai will select the whole while loop
- vaI will select the whole fragment
Region narrowing
The displayed text of a buffer can be narrowed with the commands
(start with n):
| Key Binding | Description |
|---|---|
| SPC n f | narrow the buffer to the current function |
| SPC n p | narrow the buffer to the visible page |
| SPC n r | narrow the buffer to the selected text |
| SPC n w | widen, i.e show the whole buffer again |
Line formatting
Spacemacs performs go to the line below point and indent it with
SPC j k.
You may repeat this operation with evil-repeat if you need to indent many lines.
Line formatting commands start with j:
Key Binding | Description
---------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ J | join the current line with the next line SPC j j | same as SPC j k but will split the current line at point SPC J | split a quoted string or s-expression in place SPC j J | split a quoted string or s-expression and auto-indent SPC j k | go to next line and indent it using auto-indent rules
Used together these key bindings are very powerful to quickly reformat the code.
Auto-completion
Spacemacs uses auto-complete auto-completion engine.
Key Binding | Description
-------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ C-j | select next candidate C-k | select previous candidate TAB | expand selection or select next candidate S-TAB | select previous candidate return | complete word, if word is already completed insert a carriage return
Replacing text with iedit
Spacemacs uses the powerful iedit mode through evil-iedit-state to
quickly edit multiple occurrences of a symbol or selection.
evil-iedit-state defines two new evil states:
iedit stateiedit-insert state
The color code for these states is red.
evil-iedit-state has also a nice integration with expand-region for quick
edition of the current selected text by pressing e.
iedit states key bindings
State transitions
Key Binding | From | To
-------------------|:------------------:|:-------------------------: SPC s e | normal or visual | iedit e | expand-region | iedit ESC | iedit | normal C-g | iedit | normal fd | iedit | normal ESC | iedit-insert | iedit C-g | iedit-insert | normal fd | iedit-insert | normal
To sum-up, in iedit-insert state you have to press ESC twice to
go back to the normal state. You can also at any time press C-g
or fd to return to normal state.
Note: evil commands which switch to insert state will switch in
iedit-insert state.
In iedit state
iedit state inherits from normal state, the following key bindings are
specific to iedit state.
Key Binding | Description
------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
ESC | go back to normal state
TAB | toggle current occurrence
0 | go to the beginning of the current occurrence
$ | go to the end of the current occurrence
# | prefix all occurrences with an increasing number (SPC u to choose the starting number).
A | go to the end of the current occurrence and switch to iedit-insert state
D | delete the occurrences
F | restrict the scope to the function
gg | go to first occurrence
G | go to last occurrence
I | go to the beginning of the current occurrence and switch to iedit-insert state
J | increase the edition scope by one line below
K | increase the edition scope by one line above
L | restrict the scope to the current line
n | go to next occurrence
N | go to previous occurrence
p | replace occurrences with last yanked (copied) text
S | (substitute) delete the occurrences and switch to iedit-insert state
V | toggle visibility of lines with no occurrence
U | Up-case the occurrences
C-U | down-case the occurrences
Note: 0, $, A and I have the default Vim behavior when used outside of an occurrence.
In iedit-insert state
Key Binding | Description
---------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
ESC | go back to iedit state
C-g | go back to normal state
Examples
- manual selection of several words then replace: v w w SPC s e S "toto" ESC ESC
- append text to a word on two lines: v i w SPC s e J i "toto" ESC ESC
- substitute symbol with expand-region: SPC v v e S "toto" ESC ESC
- replace symbol with yanked (copied) text with expand region: SPC v e p ESC ESC
Commenting
Comments are handled by evil-nerd-commenter, it's bound to the following keys.
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC ; | comment operator SPC c i | comment invert SPC c l | comment lines SPC c p | comment paragraphs SPC c r | comment region SPC c t | comment to line SPC c y | comment and yank
Tips: To comment efficiently a block of line use the combo:
<SPC> ; <SPC> l
Deleting files
Deletion is configured to send deleted files to system trash.
On OS X the trash program is required. It can be installed with
[homebrew][] with the following command:
$ brew install trash
To disable the trash you can set the variable delete-by-moving-to-trash
to nil in your ~/.spacemacs.
Editing Lisp code
Edition of lisp code is provided by evil-lisp-state.
Commands will set the current state to lisp state where
different commands combo can be repeated without pressing on
SPC m.
When in lisp state the color of the mode-line changes to pink.
Examples:
- to slurp three times while in normal state: SPC k 3 n
- to wrap a symbol in parenthesis then slurping two times: SPC k w 2 n
Note The lisp state commands are available in any modes! Try it out.
Lisp Key Bindings
Lisp state key bindings
These commands automatically switch to lisp state.
| Key Binding | Function |
|---|---|
| SPC k % | evil jump item |
| SPC k : | ex command |
| SPC k ( | insert expression before (same level as current one) |
| SPC k ) | insert expression after (same level as current one) |
| SPC k $ | go to the end of current sexp |
| SPC k 0 | go to the beginning of current sexp |
| SPC k a | absorb expression |
| SPC k b | forward barf expression |
| SPC k B | backward barf expression |
| SPC k c | convolute expression |
| SPC k ds | delete symbol |
| SPC k Ds | backward delete symbol |
| SPC k dw | delete word |
| SPC k Dw | backward delete word |
| SPC k dx | delete expression |
| SPC k Dx | backward delete expression |
| SPC k e | unwrap current expression and kill all symbols after point |
| SPC k E | unwrap current expression and kill all symbols before point |
| SPC k h | previous symbol |
| SPC k i | switch to insert state |
| SPC k I | go to beginning of current expression and switch to insert state |
| SPC k j | next closing parenthesis |
| SPC k J | join expression |
| SPC k k | previous opening parenthesis |
| SPC k l | next symbol |
| SPC k p | paste after |
| SPC k P | paste before |
| SPC k r | raise expression (replace parent expression by current one) |
| SPC k s | forwared slurp expression |
| SPC k S | backward slurp expression |
| SPC k t | transpose expression |
| SPC k u | undo |
| SPC k C-r | redo |
| SPC k v | switch to visual state |
| SPC k V | switch to visual line state |
| SPC k C-v | switch to visual block state |
| SPC k w | wrap expression with parenthesis |
| SPC k W | unwrap expression |
| SPC k y | copy expression |
Emacs lisp specific key bindings
| Key Binding | Function |
|---|---|
| SPC m e $ | go to end of line and evaluate last sexp |
| SPC m e e | evaluate last sexp |
| SPC m e f | evaluate current defun |
| SPC m g g | go to definition |
| SPC m h h | describe elisp thing at point (show documentation) |
| SPC m t b | execute buffer tests |
| SPC m t q | ask for test function to execute |
Managing projects
Projects in Spacemacs are managed with projectile. In
projectile projects are defined implicitly, for instance the root of a
project is found when a .git repository or .projectile file is
encountered in the file tree.
Helm is used whenever it is possible.
To search in a project see project searching.
projectile commands start with p:
Key Binding | Description
--------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
SPC p / | run ag
SPC p a | run ag
SPC p A | run ack
SPC p b | switch to project buffer
SPC p d | find directory
SPC p D | open project root in dired
SPC p f | find file
SPC p g | run grep
SPC p h | find file using helm
SPC p I | invalidate the projectile cache
SPC p j | find a tag
SPC p k | kill all project buffers
SPC p o | run multi-occur
SPC p R | regenerate the project's [e|g]tags
SPC p r | replace a string
SPC p s | switch project
SPC p t | find tags
SPC p T | find test files
SPC p v | open project root in vc-dir or magit
Registers
Access commands to the various registers start with r:
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC r e | show evil yank and named registers SPC r m | show marks register SPC r r | show helm register SPC r y | show kill ring
Errors handling
Spacemacs uses Flycheck to gives error feedback on the fly.
The checks are only performed at save time by default.
Errors management commands (star with e):
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
SPC e c | clear all errors
SPC e f | toggle flycheck
SPC e l | display the flycheck list of errors/warnings
SPC e n | go to the next error
SPC e p | go to the previous error
Custom fringe bitmaps:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Error |
 |
warning |
 |
Info |
Compiling
Spacemacs binds a few commands to support compiling a project.
Key Binding | Description
---------------------|------------------------------------------------------------
SPC c c | use helm-make via projectile
SPC c C | compile
SPC c r | recompile
Modes
Major Mode leader key
Key bindings specific to the current major mode start with SPC m.
For convenience a shortcut key called the major mode leader key is set by
default on , which saves one precious keystroke.
It is possible to change the major mode leader key by defining the variable
dotspacemacs-major-mode-leader-key in your ~/.spacemacs. For example to
setup the key on tabulation:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-major-mode-leader-key "<tab>")
Helm
Spacemacs add hjkl navigation to helm buffers:
Key Binding | Description
------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ CTRL+h | go to previous page CTRL+j | go to previous item CTRL+k | go to next item CTRL+l | go to next page
Org
In org, evil-org-mode is activated.
Key Binding | Description
----------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC m a | org-agenda SPC m A | org-archive-subtree SPC m c | org-capture SPC m C | evil-org-recompute-clocks SPC m d | org-deadline SPC m e | org-export-dispatch SPC m i | org-clock-in SPC m l | evil-org-open-links SPC m m | org-ctrl-c-ctrl-c SPC m o | org-clock-out SPC m r | org-refile SPC m s | org-schedule SPC m t | org-show-todo-tree gh | outline-up-heading gj | org-forward-heading-same-level gk | org-backward-heading-same-level gl | outline-next-visible-heading t | org-todo T | org-insert-todo-heading nil H | org-beginning-of-line L | org-end-of-line o | always-insert-item O | org-insert-heading $ | org-end-of-line ^ | org-beginning-of-line < | org-metaleft > | org-metaright TAB | org-cycle M-l | org-metaright M-h | org-metaleft M-k | org-metaup M-j | org-metadown M-L | org-shiftmetaright M-H | org-shiftmetaleft M-K | org-shiftmetaup M-J | org-shiftmetadown M-o | org-insert-heading+org-metaright M-t | org-insert-todo-heading nil+ org-metaright
Python
Writing python code with spacemacs is supported by python contribution. Please see python contribution documentation for detail.
JavaScript
More featured JavaScript support is provided by the javascript contribution. Please see javascript contribution documentation for detail.
rcirc
Key Binding | Description
------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ CTRL+j | next item in command history CTRL+k | previous item in command history
HTML and CSS
HTML contribution provides support for editing HTML, CSS, Scss and Less files. Please see html contribution documentation for detail.
Emacs Server
Spacemacs starts a server at launch. This server is killed whenever you close
your Emacs windows.
Connecting to the Emacs server
TODO
Keeping the server alive
It is possible to keep the server alive when you close Emacs by setting the
variable dotspacemacs-persistent-server to t in your ~./spacemacs.
(setq-default dotspacemacs-persistent-server t)
When this variable is set to t, the only way to quit Emacs and kill the
server is to use the following bindings:
Key Binding | Description
-------------------|------------------------------------------------------------ SPC q q | Quit Emacs and kill the server, prompt for changed buffers to save SPC q Q | Quit Emacs and kill the server, lose all unsaved changes. SPC q s | Save the buffers, quit Emacs and kill the server SPC q z | Kill the current frame
Troubleshoot
Loading fails
If during the first boot of Emacs nothing seems to happen or if the
installation seems to abort prematurely, you can check for an error message
by opening the *Warning* buffer:
C-x b warning RET
('C-x b' means 'Ctrl + x then b' and 'RET' means 'return')
Then you can copy/paste the error in a Github issue, thank you.
I have no file ~/.spacemacs
You have to manually copy the ~/.emacs.d/core/templates/.spacemacs.template
file to ~/.spacemacs
Tips
evil-lisp-state as default state
To Make lisp state the default state in Emacs Lisp buffers, insert in
your ~/.spacemacs the following snippet:
(defun dotspacemacs/config ()
(add-hook 'emacs-lisp-mode-hook 'evil-lisp-state))
Achievements
| Achievements | Account |
|---|---|
| First contribution | trishume |
| First contribution layer | trishume |
| First blog article on Spacemacs | Wolfy87 |
| First contributed banner | chrisbarrett |
| 100th issue (PR) | danielwuz |
| 200th issue (question) | justrajdeep |
| 300th issue (PR) | danielwuz |
| 400th issue (PR) | CestDiego |
| 500th issue (PR) | bjarkevad |
| 600th issue (PR) | bjarkevad |
| 100th pull request | bru |
| 200th pull request | smt |
| 300th pull request | [BrianHicks][] |
| PR gunner (8 PRs in a row) | ralesi |
| 100th fork | balajisivaraman |
| 100th star | Jackneill |
| 200th star | jb55 |
| 400th star | dbohdan |
| 600th star | laat |
| 700th star | [kendall][] |
Thank you
Jokes aside, thank you Richard for this great piece of software.
Thank you to all the contributors and the whole Emacs community from core developers to elisp hackers!